Learning how to manage anger naturally offers a holistic approach to achieving emotional balance and improving overall well-being. By exploring various techniques rooted in mindfulness, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional awareness, individuals can effectively reduce anger without reliance on medication. This comprehensive guide provides practical strategies and insights to help you cultivate a calmer, more resilient mindset.
Understanding and implementing natural anger management methods can lead to healthier relationships, enhanced mental clarity, and a more peaceful life. From recognizing personal triggers to adopting calming routines, empowering yourself with these techniques can transform your emotional responses and promote lasting tranquility.
Understanding Natural Anger Management Techniques
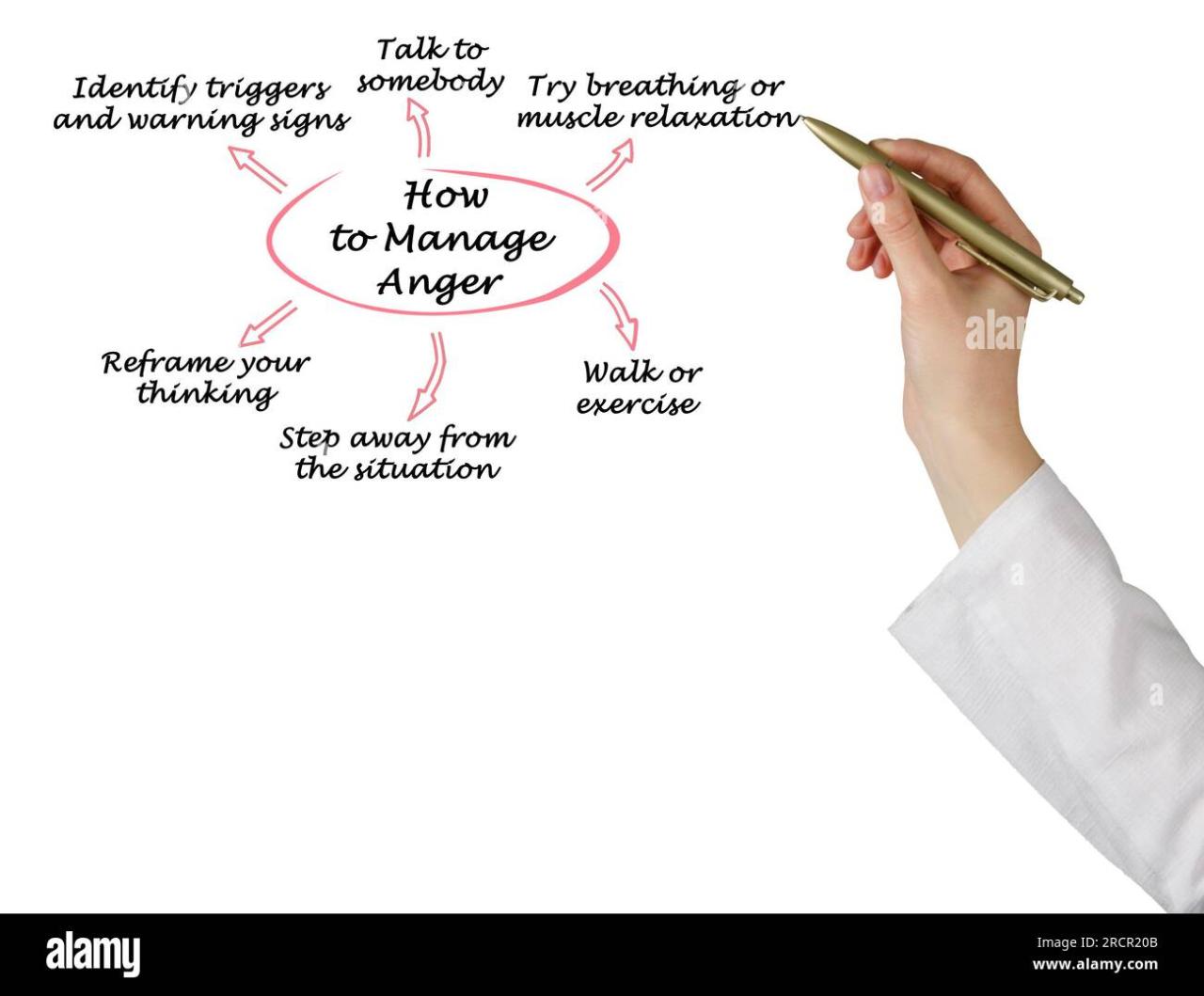
Managing anger effectively without reliance on medication involves embracing holistic approaches that promote mental and physical well-being. These techniques aim to calm the mind, relax the body, and foster emotional resilience, enabling individuals to respond to stressors with clarity and composure. By incorporating natural methods into daily routines, people can reduce the intensity and frequency of anger episodes, leading to healthier relationships and improved quality of life.
Various holistic strategies focus on nurturing the body’s innate capacity to regulate emotions through mindfulness, physical activity, and breathing exercises. These methods are accessible, cost-effective, and free of side effects, making them suitable for long-term use. Understanding and practicing these techniques can empower individuals to handle anger constructively while enhancing overall mental health.
Holistic Approaches to Reduce Anger
Several natural techniques have proven effective in managing anger by promoting relaxation, increasing self-awareness, and reducing physiological arousal associated with emotional outbursts. These approaches are often used alone or in combination, tailored to individual preferences and circumstances. Common methods include meditation, deep breathing exercises, and physical activity, each offering unique benefits and application strategies.
| Technique | Description | Benefits | Implementation Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meditation | A mindfulness practice that involves focusing attention and eliminating distractions to achieve mental clarity and emotional calm. | Reduces stress, improves emotional regulation, enhances self-awareness, lowers blood pressure. | Find a quiet space, sit comfortably, close your eyes, and focus on your breath or a calming word or phrase. Practice for 10-15 minutes daily. |
| Deep Breathing | Controlled breathing exercises that involve slow, deliberate inhalation and exhalation to activate relaxation responses. | Decreases physiological arousal, reduces feelings of anger, improves focus, lowers cortisol levels. | Inhale slowly through the nose for four counts, hold the breath for four counts, then exhale slowly through the mouth for four counts. Repeat for 5-10 minutes during moments of anger. |
| Physical Exercise | Engaging in activities such as walking, jogging, yoga, or martial arts to release built-up tension and improve mood. | Relieves stress, boosts endorphins, improves overall health, and reduces irritability. | Participate in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise several times a week. Incorporate activities that you enjoy to ensure consistency. |
In everyday routines, integrating these natural anger management practices can lead to significant improvements in emotional stability. For example, starting each day with a short meditation session can set a calm tone for the hours ahead. During stressful work interactions, taking a few deep breaths before responding can prevent escalation. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as evening walks or weekend yoga classes, not only enhances physical health but also fosters emotional resilience.
Over time, these routines contribute to a more balanced temperament, better stress handling, and healthier interpersonal relationships.
Identifying Triggers and Emotional Patterns
Effective anger management begins with the ability to recognize the specific situations, behaviors, or thoughts that tend to provoke feelings of anger. By understanding personal triggers and emotional warning signs, individuals can develop targeted strategies to prevent escalation and maintain emotional balance. This process involves attentive self-monitoring and reflection, often facilitated through journaling exercises that help clarify patterns and insights over time.
Recognizing these triggers and patterns not only aids in immediate calming responses but also contributes to long-term emotional resilience. When individuals become aware of the early signs of anger, they can employ coping mechanisms proactively, leading to healthier interactions and overall well-being.
Identifying Personal Anger Triggers
Personal triggers are specific stimuli that consistently evoke feelings of anger. These vary widely among individuals and can include external events or internal thoughts. Using journaling exercises to record daily experiences enables individuals to pinpoint recurring triggers and understand their emotional responses more clearly.
To identify triggers effectively, it is recommended to keep a dedicated journal, noting down instances of anger along with the context and feelings experienced before, during, and after the event. This reflective practice helps uncover patterns, such as particular people, situations, or internal thoughts that tend to set off anger episodes.
Common Anger Triggers with Descriptions and Coping Strategies
Below is a list of common triggers that frequently lead to anger, accompanied by brief descriptions and suggested strategies for managing each:
- Feeling Disrespected: When someone dismisses or belittles you.
Strategy: Practice assertive communication and remind yourself of your self-worth. - Frustration Over Unmet Expectations: When plans or goals are blocked or delayed.
Strategy: Cultivate patience and adapt expectations to be more flexible. - Perceived Injustice: Witnessing unfair treatment or inequality.
Strategy: Engage in constructive dialogue or advocacy, and focus on what can be controlled. - Overwhelming Workload: Facing excessive demands or tight deadlines.
Strategy: Prioritize tasks, delegate when possible, and take scheduled breaks. - Relationship Conflicts: Disagreements or misunderstandings with loved ones.
Strategy: Use active listening and calm, respectful expression of feelings. - Environmental Stressors: Noise, chaos, or uncomfortable surroundings.
Strategy: Create a calm environment when possible and employ relaxation techniques.
Tracking Triggers, Emotions, and Calming Techniques
Implementing a systematic approach to monitor and analyze anger episodes can significantly improve awareness and response. The following table provides a structured method to record triggers, emotional reactions, and effective calming strategies, facilitating ongoing self-awareness and skill development.
| Trigger | Emotional Response | Calming Technique Used | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Being interrupted during a meeting | Frustration, irritation | Deep breathing, pausing before responding | Calmed down, responded assertively without anger |
| Disagreement with a partner | Disappointment, anger | Taking a walk, practicing mindfulness | Reduced intensity of anger, fostered constructive conversation |
| Traffic jam delaying arrival | Impatience, annoyance | Listening to calming music, focusing on breath | Maintained composure, avoided escalation of frustration |
| Workload exceeding capacity | Stress, irritability | Prioritization, short breaks for stretching | Regained focus, prevented anger from building up |
Tracking triggers and responses allows for targeted strategies and fosters greater self-awareness, ultimately helping to manage anger more effectively over time.
Developing Mindfulness and Relaxation Strategies
Implementing mindfulness and relaxation techniques offers a powerful approach to managing anger naturally. These strategies help individuals cultivate awareness of their emotional state, reduce physiological arousal, and foster a sense of calmness even in challenging situations. Consistent practice can significantly diminish the intensity and frequency of anger episodes, leading to healthier emotional responses.
By integrating mindfulness and relaxation routines into daily life, individuals can develop a proactive approach to emotional regulation. These methods not only serve as immediate calming tools but also enhance overall emotional resilience, making it easier to navigate conflicts and stressors with composure.
Cultivating Mindfulness through Guided Meditation and Breathing Exercises
Mindfulness involves paying deliberate, non-judgmental attention to the present moment. Guided meditation and breathing exercises are accessible techniques that can be practiced daily to foster greater awareness and control over emotional responses. Regular engagement with these practices helps individuals recognize early signs of anger and respond thoughtfully rather than impulsively.
Guided meditation scripts typically focus on breathing, body awareness, and visualization, guiding the practitioner to observe their thoughts and feelings without attachment. Breathing exercises, on the other hand, emphasize slow, deep breaths that activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and emotional stability.
Guided Meditation Script
Find a comfortable seated position, ensuring your back is straight but relaxed. Close your eyes gently and take a deep breath in through your nose, filling your lungs completely. Hold the breath for a count of three, then slowly exhale through your mouth, releasing tension. Repeat this cycle, focusing solely on your breath. As thoughts arise, acknowledge them without judgment and gently bring your attention back to your breathing.
Continue this process for five to ten minutes, allowing yourself to become more centered and calm.
Breathing Exercise: The 4-7-8 Technique
This simple yet effective breathing pattern can be employed whenever feelings of anger begin to surface. It involves:
- Inhaling quietly through the nose for a count of 4.
- Holding the breath for a count of 7, allowing your lungs to fill completely and your mind to focus on the sensation of breath retention.
- Exhaling fully and audibly through the mouth for a count of 8, releasing all tension and unhelpful energy.
Repeat this cycle three to four times. This technique slows the heart rate, reduces anxiety, and creates a sense of calm, making it easier to respond to anger-provoking situations with clarity and composure.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation Technique
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) systematically tenses and relaxes different muscle groups, helping reduce physical tension associated with anger responses. This method fosters awareness of bodily sensations and promotes relaxation, which can prevent escalation of emotional episodes.
Follow these detailed steps for effective PMR practice:
- Prepare: Sit or lie down in a quiet, comfortable space. Close your eyes and take a few deep breaths to center yourself.
- Feet and Legs: Tense the muscles in your feet by curling your toes tightly, hold for 5 seconds, then release slowly, noticing the contrast.
- Thighs: Squeeze your thigh muscles by pressing your knees together or contracting the quadriceps, hold for 5 seconds, then release.
- Abdomen and Chest: Tighten your abdominal muscles by pulling your belly button inward, hold, then relax.
- Hands and Arms: Clench your fists tightly, hold for 5 seconds, then open your hands and relax.
- Shoulders and Neck: Raise your shoulders toward your ears, hold, then drop them back to a relaxed position.
- Facial Muscles: Scrunch your face, squeezing your eyes shut and opening your mouth wide, hold, then relax your facial muscles.
Concluding the session, take a few deep breaths and notice the overall sense of relaxation. Practice PMR regularly to build a conditioned response that helps lower physiological arousal during stressful or anger-inducing events.
Visual Flowchart: Progression from Anger Onset to Calming through Mindfulness
Recognize the rising anger and initiate controlled breathing to stabilize emotional response.
Engage in guided meditation or focus on deep breathing, observing sensations without judgment.
Complete progressive muscle relaxation to release physical tension, reinforcing calmness.
Return to emotional balance with a sense of control and readiness to respond thoughtfully.
Incorporating Lifestyle Changes for Better Anger Management

Managing anger effectively often requires a holistic approach that integrates healthy lifestyle habits. Recognizing how nutrition, sleep, and physical activity influence emotional regulation can significantly enhance your ability to maintain calmness in challenging situations. Implementing practical adjustments in these areas can lead to noticeable improvements in overall emotional well-being and reduce the frequency and intensity of anger episodes.A balanced lifestyle supports the body’s natural capacity to regulate emotions, reduce stress levels, and foster resilience.
By making mindful choices regarding diet, sleep routines, and physical activity, individuals can create a solid foundation for sustained anger management and emotional stability.
Nutrition’s Role in Anger Regulation
A nutritious diet provides essential nutrients that support brain health and hormonal balance, which are crucial in managing emotions. Deficiencies in nutrients such as magnesium, omega-3 fatty acids, and B vitamins have been associated with increased irritability and mood swings. To optimize emotional stability through nutrition:
- Consume foods rich in magnesium, including leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, to promote relaxation and reduce stress.
- Incorporate omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, which have been linked to decreased aggression and improved mood.
- Limit intake of processed foods, excessive caffeine, and sugar, as they can cause blood sugar fluctuations and irritability.
- Maintain regular meal times to stabilize blood glucose levels, preventing mood swings related to hunger or hypoglycemia.
Sleep and Its Impact on Anger Control
Adequate and quality sleep is fundamental for emotional regulation. Sleep deprivation or poor sleep quality can heighten emotional reactivity and impair judgment, leading to increased anger response. Effective strategies to improve sleep include:
- Establishing a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time daily, even on weekends.
- Avoiding electronic devices at least an hour before bedtime to reduce blue light exposure, which can interfere with melatonin production.
- Creating a calming bedtime routine, such as reading or practicing gentle stretches, to signal the body that it’s time to wind down.
- Ensuring the sleep environment is comfortable, dark, and cool to promote restful sleep.
Physical Activity as a Natural Anger Outlet
Regular physical activity releases endorphins and reduces stress hormones like cortisol, thereby enhancing mood and emotional resilience. Exercise can serve as an effective outlet for pent-up frustration and help in managing anger constructively.Practical ways to incorporate physical activity include:
- Engaging in aerobic exercises such as brisk walking, running, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week.
- Practicing yoga or tai chi, which combine movement with mindfulness, to cultivate relaxation and mental clarity.
- Participating in team sports or group fitness classes to promote social connection and emotional support.
- Incorporating short bouts of activity, such as stretching or quick walks, during the workday to break tension and reset mood.
Natural Supplements and Herbal Remedies for Emotional Balance
Certain natural supplements and herbs are recognized for their calming properties and ability to support emotional stability, potentially reducing anger and irritability when used appropriately.Common options include:
- Valerian Root: Known for its sedative effects, it can help improve sleep quality. Usage typically involves taking 400-900 mg before bedtime, but consultation with a healthcare provider is advised.
- Passionflower: Contains compounds that promote relaxation. It can be consumed as a tea or supplement, usually at doses of 250-500 mg daily.
- Magnesium Supplements: Support nerve function and relaxation. Daily doses of 200-400 mg are generally safe, but it is best to start with a low dose and increase gradually under medical guidance.
- Rhodiola Rosea: An adaptogen that reduces fatigue and stress. Typical dosages range from 200-400 mg per day, taken in the morning or early afternoon.
- Lavender: Aromatherapy with lavender essential oil can calm nerves and reduce anxiety. Diffusing lavender or applying diluted oil to pulse points can be effective.
Note
* Always consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any new supplement or herbal remedy, especially if taking medications or managing chronic health conditions.
Lifestyle Modification Summary
| Modification | Effects on Anger | Practical Implementation Ideas |
|---|---|---|
| Balanced Nutrition | Reduces irritability, stabilizes mood, supports brain health | Include magnesium-rich foods, omega-3 sources, and minimize processed foods |
| Quality Sleep | Decreases emotional reactivity, enhances patience | Maintain consistent sleep schedule, create calming routines, optimize sleep environment |
| Regular Physical Activity | Reduces stress, releases endorphins, improves mood | Engage in aerobic exercises, yoga, or team sports regularly |
| Natural Supplements & Herbs | Promotes relaxation, improves emotional balance | Use valerian root, passionflower, magnesium, or lavender as directed, with professional guidance |
Building Emotional Resilience and Positive Habits

Developing emotional resilience is essential for managing anger naturally and maintaining emotional balance in daily life. By cultivating positive habits and integrating mindful routines, individuals can better navigate stressors and emotional triggers, leading to a more peaceful and controlled response to challenging situations.
Fostering resilience involves consistent effort and the adoption of practices that reinforce emotional strength. These habits not only support anger management but also contribute to overall mental well-being, enabling individuals to respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively. Establishing a structured plan to incorporate these habits into everyday life ensures sustainable progress and emotional stability.
Methods to Strengthen Emotional Resilience Through Daily Routines and Practices
Building emotional resilience requires intentional daily activities that reinforce positive emotional states and coping mechanisms. These methods help individuals develop a buffer against stress and reduce the likelihood of anger escalation.
- Practicing Gratitude Regularly: Starting each day by noting three things you are grateful for shifts focus from negative triggers to positive aspects of life, fostering a resilient mindset. Maintaining a gratitude journal can reinforce this habit.
- Engaging in Stress Management Techniques: Incorporating brief breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or mindfulness meditation into daily routines can significantly lower stress levels. For example, dedicating 10 minutes each morning to deep breathing prepares you to handle daily frustrations calmly.
- Maintaining Consistent Physical Activity: Regular exercise, such as walking, yoga, or swimming, releases endorphins that elevate mood and improve emotional regulation. Engaging in physical activity at least three times per week enhances resilience over time.
- Prioritizing Adequate Sleep and Nutrition: Ensuring sufficient rest and balanced nutrition stabilizes mood and reduces irritability, which are common precursors to anger.
Creating a Positive Habit Formation Plan with Timeframes and Activities
Establishing consistent routines involves setting realistic goals and tracking progress over specific periods. A structured plan helps embed positive habits that support natural anger control and emotional resilience.
- Week 1-2: Foundation Phase: Focus on daily gratitude journaling each morning and practicing 5-minute mindful breathing sessions twice daily. Include light physical activity, such as daily 15-minute walks.
- Week 3-4: Reinforcement Phase: Extend mindfulness sessions to 10 minutes and add a weekly yoga or stretching class. Continue gratitude practices and monitor sleep quality and nutrition.
- Week 5-6: Intensification and Reflection: Introduce journaling to identify emotional patterns and triggers, alongside daily stress management techniques. Evaluate progress and adjust routines to fit personal preferences.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting habits ensures sustained motivation and effectiveness. Celebrating small milestones fosters a positive attitude towards ongoing emotional development.
Weekly Planner for Tracking Emotional Resilience Exercises
| Day of Week | Gratitude Journaling | Mindfulness/Breathing | Physical Activity | Sleep & Nutrition | Notes/Reflections |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | ✓ | ✓ | Walk (20 min) | 7-8 hrs, balanced meal | Noted increased calmness after exercises |
| Tuesday | ✓ | ✓ | Yoga (30 min) | 7 hrs, healthy snacks | Managed a stressful situation better than usual |
| Wednesday | ✓ | ✓ | Jogging (25 min) | 7.5 hrs, nutritious dinner | Felt more resilient during a disagreement |
| Thursday | ✓ | ✓ | Stretching & Meditation (15 min) | 8 hrs, balanced diet | Noticed improved sleep quality |
| Friday | ✓ | ✓ | Walking (30 min) | 7 hrs, hydration focus | Handled minor frustrations calmly |
| Saturday | ✓ | ✓ | Yoga or recreational activity | 8 hrs, nutritious breakfast | Reflected on weekly progress, set next goals |
| Sunday | ✓ | ✓ | Rest or light activity | 7-8 hrs, healthy meals | Prepared plan for upcoming week |
This planner facilitates consistent tracking, allowing individuals to observe patterns, identify effective practices, and stay motivated on their journey to building emotional resilience and maintaining positive habits that naturally support anger management.
Communicating Effectively to Reduce Anger

Effective communication plays a vital role in managing and reducing anger, especially during disagreements or heated situations. When individuals learn to express themselves assertively and listen actively, conflicts are less likely to escalate into overt anger. Developing these skills fosters understanding, promotes emotional regulation, and paves the way for constructive interactions even amid tension.
Implementing practical communication techniques empowers individuals to handle conflicts with calmness and clarity. This section explores assertive communication, conflict resolution strategies, and provides illustrative dialogues to demonstrate how thoughtful responses can de-escalate anger and foster healthier relationships.
Assertive Communication and Conflict Resolution Techniques
Mastering assertive communication involves expressing one’s thoughts and feelings honestly while respecting others’ perspectives. This approach prevents misunderstandings and helps avoid passive or aggressive responses that often intensify anger. Conflict resolution strategies focus on addressing issues directly and collaboratively, aiming for mutual understanding and solutions.
Effective communication during moments of anger requires specific skills:
- Express yourself clearly and calmly: Use “I” statements to convey feelings without blame.
- Practice active listening: Show genuine interest in understanding the other person’s viewpoint.
- Maintain a respectful tone: Avoid sarcasm, insults, or raised voices.
- Seek common ground: Focus on shared goals or interests to facilitate cooperation.
- Know when to pause: Allow yourself time to cool down before responding if emotions run high.
Conflict resolution can be systematically approached through structured strategies that promote constructive dialogue:
- Identify the core issue: Understand what is truly causing the frustration.
- Express concerns assertively: Use calm language to state your feelings and needs.
- Practice empathetic listening: Repeat or paraphrase what the other person shares to confirm understanding.
- Seek mutually beneficial solutions: Brainstorm options that satisfy both parties.
- Agree on actionable steps: Confirm commitments to resolve the issue and prevent future conflicts.
Sample Dialogues Demonstrating Calming Responses and Constructive Interactions
Below are example exchanges that depict effective communication strategies in tense situations, illustrating how calm responses can defuse anger and promote resolution:
Scenario 1: A colleague criticizes your work during a team meeting.
Colleague: “Your report was incomplete and careless.”
You: “I understand your concerns. I might have missed some details, and I appreciate your feedback. Let me review the report and address any gaps.”
Scenario 2: A family member raises their voice during a disagreement.
Family Member: “You never listen to me!”
You: “I hear that you’re upset, and I want to understand your perspective. Please tell me what’s bothering you so we can work through it together.”
These dialogues exemplify calm, respectful, and assertive communication that helps prevent escalation and encourages collaborative problem-solving. Maintaining composure, using “I” statements, and showing empathy are key elements in fostering effective interactions during emotionally charged moments.
Ultimate Conclusion
Incorporating these natural strategies into your daily routine can significantly improve your ability to manage anger constructively. By fostering mindfulness, making positive lifestyle changes, and enhancing emotional resilience, you create a sustainable path toward emotional harmony. Embrace these practices to enjoy a more balanced and peaceful life, free from unnecessary stress and conflict.