Discovering how to sleep better without medication offers a natural pathway to achieving restorative and consistent rest. Many individuals face challenges with sleep, often turning to pharmaceuticals that may carry unwanted side effects. Exploring holistic approaches can empower you to enhance your sleep quality through understanding your body’s natural rhythms and creating an environment conducive to relaxation.
This guide delves into practical strategies, including optimizing your sleep environment, establishing calming routines, making mindful dietary choices, and employing relaxation techniques. By adopting these methods, you can improve your sleep naturally and foster overall health and well-being.
Understanding Natural Sleep Cycles

Achieving restful sleep involves more than just the number of hours spent in bed; it requires a comprehensive understanding of the natural processes your body undergoes during sleep. Recognizing these cycles can help you optimize your sleep quality and foster habits that support your overall health and well-being. By aligning your routines with your body’s intrinsic rhythms, you can enhance restorative sleep without the need for medication.
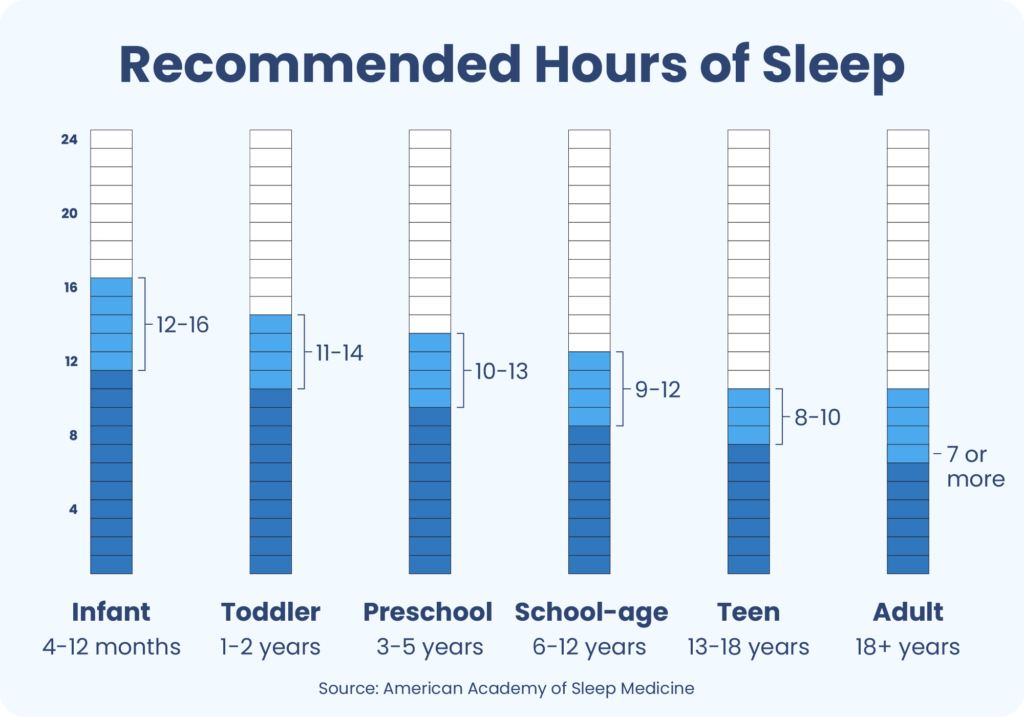
Sleep is a dynamic state characterized by distinct stages that repeat throughout the night, each playing a vital role in physical and mental health. Additionally, your body’s internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm, governs the timing of these stages. Disruptions to these natural cycles can lead to various health issues, including impaired cognitive function, weakened immunity, and increased risk of chronic conditions.
Stages of Sleep and Their Impact on Rest
Understanding the progression through different sleep stages sheds light on their importance in achieving deep, restorative rest. These stages include non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, each contributing uniquely to overall health.
During a typical sleep cycle, which lasts approximately 90 minutes, the body transitions through several phases:
- Stage 1 (Light Sleep): This initial phase marks the transition from wakefulness to sleep. Characterized by slow eye movements and decreased muscle activity, it helps you relax and prepare for deeper sleep stages. Typically lasting around 5-10 minutes, it constitutes about 5% of total sleep.
- Stage 2 (Light Sleep): Body temperature drops, heart rate slows, and breathing becomes more regular. This stage accounts for roughly 45-55% of total sleep and is crucial for memory consolidation and energy restoration.
- Stages 3 & 4 (Deep Sleep or Slow-Wave Sleep): These stages involve slow brain waves called delta waves. Deep sleep strengthens the immune system, repairs tissues, and promotes physical recovery. It also plays a vital role in memory retention and cognitive function. Deep sleep typically occupies about 15-20% of a sleep cycle.
- REM Sleep: Characterized by rapid eye movements, vivid dreaming, and increased brain activity, REM sleep supports emotional regulation and memory processing. It generally makes up 20-25% of total sleep time and occurs after periods of deep sleep.
Disruption in any of these stages can compromise sleep quality, leading to fatigue, reduced alertness, and compromised immune function. Achieving a balanced progression through all stages is essential for holistic health.
Role of Circadian Rhythms in Sleep Regulation
The circadian rhythm is an internal biological clock synchronized with the 24-hour day-night cycle. It influences numerous physiological processes, including sleep-wake patterns, hormone secretion, body temperature, and metabolism. Proper alignment of this rhythm is vital for experiencing restful, uninterrupted sleep.
Key elements of circadian regulation include:
- Melatonin Production: This hormone, secreted primarily at night, signals to the body that it is time to prepare for sleep. Its levels naturally rise in the evening and fall at dawn, promoting feelings of sleepiness.
- Light Exposure: Exposure to natural light during the day helps reinforce circadian cues, while artificial light, especially blue light from screens, can suppress melatonin, delaying sleep onset.
- Consistent Sleep Schedules: Going to bed and waking up at the same times each day supports the stability of your internal clock, leading to better sleep quality.
To naturally synchronize your circadian rhythms, consider the following practices:
- Expose yourself to bright natural light early in the day to reinforce your wakefulness signals.
- Limit exposure to screens and artificial light at least two hours before bedtime.
- Maintain a regular sleep and wake schedule, even on weekends, to strengthen your internal clock.
Consequences of Disrupted Sleep Cycles on Health
Interrupted or poorly aligned sleep cycles can have significant adverse effects on physical and mental health. Chronic disruptions may lead to a range of health issues that impair daily functioning and increase disease risk.
Some of the notable consequences include:
- Cognitive Impairment: Fragmented sleep affects memory, attention, and decision-making abilities.
- Immune System Suppression: Insufficient deep and REM sleep weaken immune responses, making the body more susceptible to infections.
- Metabolic Dysregulation: Disrupted circadian rhythms are linked to increased risk of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
- Mood Disorders: Poor sleep cycles are associated with anxiety, depression, and irritability.
Maintaining natural sleep cycles is thus essential for safeguarding overall health, emphasizing the importance of sleep hygiene, consistent routines, and environmental factors that support the body’s internal timing mechanisms.
Creating a Sleep-Friendly Environment
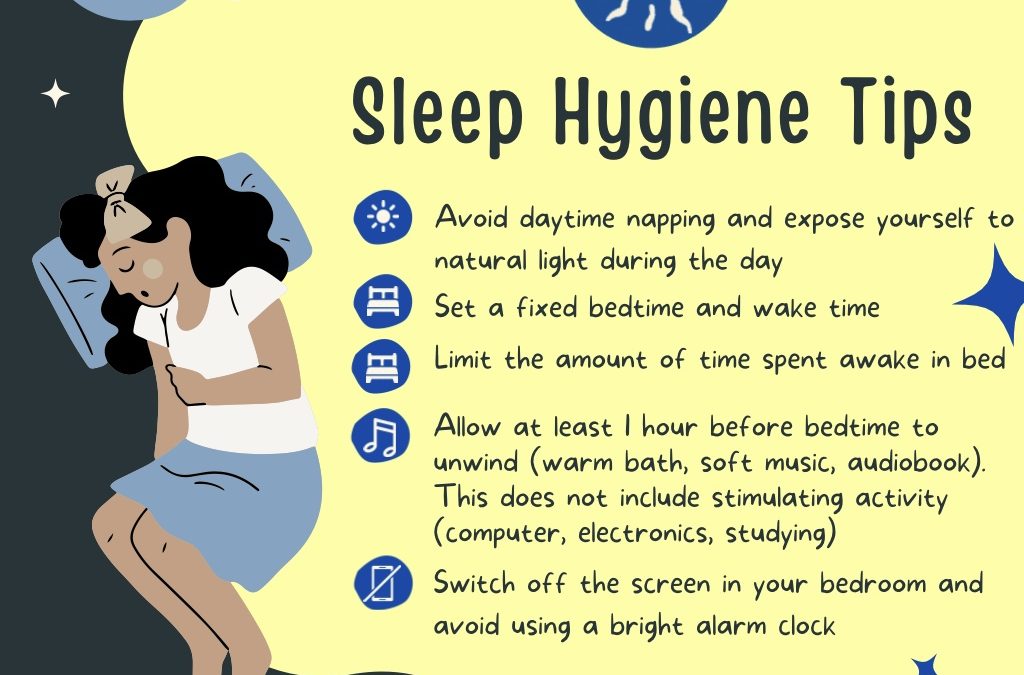
Establishing an environment conducive to restful sleep is fundamental for enhancing sleep quality without the use of medication. The right bedroom conditions can significantly influence your ability to fall asleep quickly and enjoy uninterrupted rest throughout the night. Carefully optimizing factors such as lighting, temperature, noise levels, and overall room layout can promote relaxation and facilitate natural sleep patterns.A sleep-friendly environment minimizes disturbances and supports the body’s natural circadian rhythms.
By making deliberate adjustments to your sleeping space, you create a sanctuary that signals to your brain that it is time to wind down and rest. This approach not only improves sleep onset but also enhances overall sleep quality, leading to better daytime functioning and well-being.
Optimizing Bedroom Conditions for Better Sleep
Creating an ideal sleeping environment involves attention to multiple sensory inputs and physical comfort. Proper lighting management, temperature regulation, noise control, and air quality all play vital roles in fostering a restful atmosphere.
Adjusting lighting to match natural circadian cues is essential. Lowering light levels during the evening and eliminating bright screens at least an hour before bedtime can help signal to your body that it is time to prepare for sleep. Using blackout curtains or eye masks can further reduce light exposure, especially in urban areas with streetlights or outdoor illumination.
Maintaining a comfortable temperature, typically between 16-20°C (60-68°F), supports thermoregulation, which is crucial for sleep initiation. Using fans, air purifiers, or heating devices can help maintain this optimal range, ensuring the environment remains conducive regardless of seasonal changes.
Controlling noise levels is equally important. Employing white noise machines, earplugs, or soundproofing measures can diminish disruptive sounds from traffic, household activity, or neighbors. A quiet bedroom minimizes arousal and promotes uninterrupted sleep cycles.
Fresh air circulation enhances air quality and can be achieved through proper ventilation or air purifiers, reducing indoor pollutants and allergen presence that might disturb sleep.
Decluttering and Arranging the Sleeping Area
A cluttered or disorganized bedroom can evoke feelings of chaos and hinder relaxation. Creating a clean, orderly space encourages mental calmness and physical comfort, which are essential for sleep readiness.
Follow this checklist to transform your bedroom into a serene sanctuary:
- Remove unnecessary items from the sleeping area, such as work materials, laundry, or electronic devices not used for sleep.
- Designate a specific space for sleep and keep it reserved for rest and relaxation activities only.
- Use storage solutions to keep personal belongings organized and out of sight, reducing visual clutter.
- Keep surfaces clean and dust-free to improve air quality and reduce allergens that could interfere with sleep.
- Arrange furniture to avoid obstructing airflow or creating cramped spaces; ensure that the bed is easily accessible and positioned to maximize comfort.
- Incorporate calming decor, such as soft colors, minimalistic design, and natural elements, to foster a tranquil environment.
Choosing Supportive Bedding and Comfortable Sleepwear
The physical comfort provided by your bedding and sleepwear significantly impacts sleep quality. Selecting supportive mattresses, pillows, and breathable sleepwear can reduce physical discomfort and promote restful slumber.
When choosing a mattress, opt for one that offers adequate support for your preferred sleeping position. Medium-firm mattresses are generally suitable for most people, providing a balance between softness and support. Consider materials like memory foam or latex, which conform to the body’s contours and alleviate pressure points.
Supportive pillows should align the neck and head with the spine, preventing strain or discomfort. The firmness and shape depend on your sleeping position—side sleepers benefit from thicker pillows, while back sleepers prefer medium firmness, and stomach sleepers may require softer options.
Prioritize sleepwear made from natural, breathable fabrics such as cotton, linen, or bamboo. These materials help regulate body temperature, wick away moisture, and prevent overheating during the night. Loose-fitting clothing reduces constriction, allowing for pleasant airflow and reducing discomfort.
Investing in high-quality bedding, including breathable sheets and duvet covers, enhances overall comfort. Regular washing and replacing worn-out linens ensure a clean, inviting sleeping surface that supports healthy sleep habits.
Establishing Effective Bedtime Routines
Creating a consistent and calming pre-sleep ritual is fundamental to improving sleep quality without the reliance on medication. A routine signals to your body that it is time to wind down, helping facilitate a smoother transition from wakefulness to sleep. By establishing reliable habits, you reinforce your natural sleep cues, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
Developing a structured bedtime routine involves selecting activities that promote relaxation and consistency. When these activities become habitual, they create a psychological and physiological cue that signals your body to prepare for rest. This consistency not only enhances sleep quality but also reduces nighttime awakenings and early morning awakenings, contributing to more restorative sleep cycles.
Organizing a Step-by-Step Guide to Calm Pre-Sleep Rituals
Implementing a series of calming activities before bed can significantly improve sleep onset and quality. The following step-by-step guide provides a practical approach to developing an effective pre-sleep routine:
- Set a Fixed Bedtime: Choose a consistent time to go to bed each night, even on weekends, to regulate your internal clock.
- Limit Screen Exposure: Turn off electronic devices at least 30 to 60 minutes before bed. The blue light emitted by screens suppresses melatonin production, disrupting sleep signals.
- Engage in Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate calming activities such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or gentle stretches to reduce physical tension.
- Create a Warm, Comfortable Environment: Dim the lights, adjust room temperature to a cool and comfortable level, and use soft, calming scents like lavender.
- Incorporate Quiet Activities: Read a book, listen to soothing music, or practice meditation to further relax the mind and body.
- Avoid Stimulating Substances: Refrain from caffeine, nicotine, or heavy meals close to bedtime, as these can interfere with your ability to fall asleep.
This systematic approach ensures that each step contributes to the relaxation process, gradually easing your transition into sleep.
Reinforcing Healthy Sleep Habits with Consistent Sleep and Wake Times
Maintaining a regular sleep and wake schedule is a cornerstone of healthy sleep hygiene. Consistency helps synchronize your circadian rhythm, the internal biological clock that regulates sleep-wake cycles, thereby enhancing overall sleep quality.
When your sleep and wake times are stable, your body becomes accustomed to a predictable pattern, reducing the likelihood of insomnia and fragmented sleep. For example, going to bed at 10:00 PM and waking at 6:00 AM every day supports stable melatonin production and hormone regulation, facilitating more restorative sleep stages.
“Routine and consistency are key to entraining your circadian rhythm, leading to better sleep quality and daytime alertness.”
It is important to maintain this schedule even on weekends or days off, as irregular sleep times can disrupt your internal clock, leading to difficulty falling asleep during the week and feeling groggy during the day. Establishing and adhering to fixed sleep and wake times, combined with a calming bedtime routine, creates a synergistic effect that promotes healthier sleep patterns and overall well-being.
Dietary and Lifestyle Adjustments

Achieving restful sleep often requires more than just good sleep habits; it involves mindful choices in diet and daily activities. Adjusting what and when we eat, along with incorporating healthy lifestyle practices, can significantly improve sleep quality without the need for medication. These adjustments help regulate the body’s internal clock, reduce nighttime discomfort, and promote relaxation, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep through the night.
Implementing dietary and lifestyle changes can lead to sustainable improvements in sleep, fostering overall well-being. It is essential to understand which foods and habits support healthy sleep patterns and which may hinder them, so that these can be effectively integrated into daily routines.
Foods and Beverages to Avoid Before Bed
Consuming certain foods and drinks in the hours leading up to bedtime can interfere with sleep quality by causing discomfort or stimulating the nervous system. Recognizing and limiting these items can facilitate a smoother transition into restful sleep.
- High-caffeine beverages such as coffee, tea, energy drinks, and certain sodas should be avoided at least four to six hours before bedtime, as caffeine is a stimulant that can delay sleep onset and reduce sleep quality.
- Heavy or spicy meals close to bedtime may cause indigestion, acid reflux, or discomfort, making it difficult to fall asleep peacefully.
- Alcohol, although initially sedating, can disrupt sleep cycles and lead to fragmented sleep during the night, reducing overall restfulness.
- Foods high in sugar or refined carbohydrates can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, leading to wakefulness or vivid dreams that disturb sleep patterns.
Natural Methods to Promote Sleep
Natural remedies and practices can enhance sleep quality by fostering relaxation and reducing stress without the side effects associated with medications. These methods can be integrated into daily routines to create a calming environment conducive to rest.
Herbal teas, aromatherapy, and supplements offer gentle support for sleep, helping to establish a natural and soothing bedtime ritual.
- Herbal teas: Chamomile, valerian root, lavender, and lemon balm teas are widely recognized for their calming properties. Drinking a warm cup approximately 30 minutes before bed can promote relaxation and readiness for sleep.
- Aromatherapy: Using essential oils such as lavender, bergamot, or ylang-ylang in diffusers or via massage can create a serene environment that encourages sleep. These scents are known for their anxiolytic and sedative effects.
- Supplements: Natural supplements like melatonin, magnesium, and valerian root extract are sometimes used to support sleep. It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen to ensure safety and appropriateness.
Incorporating Daytime Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity during the day not only benefits overall health but also plays a crucial role in enhancing sleep quality. Proper timing and type of activity can optimize its positive effects on sleep patterns.
Research indicates that moderate aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, helps to regulate circadian rhythms and reduces symptoms of insomnia. Exercising too close to bedtime, however, may have an arousing effect, making it harder to wind down.
- Engage in physical activity at least three hours before bedtime to allow the body to cool and relax before sleep.
- Incorporate activities that promote relaxation, such as yoga or stretching, during the evening hours to help reduce stress and prepare the body for rest.
- Consistency is key; maintaining a regular exercise schedule supports the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to more restorative sleep over time.
Stress Reduction and Relaxation Techniques
Achieving restful sleep often requires more than just managing physical and environmental factors; addressing mental and emotional stress is equally crucial. Incorporating relaxation techniques into your bedtime routine can significantly ease your transition into sleep, reduce nighttime awakenings, and promote overall sleep quality. These methods help calm the nervous system, lower cortisol levels, and foster a state of tranquility conducive to restorative rest.Engaging in relaxation exercises before sleep not only alleviates daily stress but also trains the mind and body to recognize signals for rest.
Regular practice of these techniques can lead to long-term benefits, including decreased anxiety, improved mood, and enhanced sleep efficiency.
Relaxation Exercises: Deep Breathing, Progressive Muscle Relaxation, and Meditation
Relaxation exercises harness controlled physical and mental processes to reduce tension and promote calmness. Among the most effective are deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation.
- Deep Breathing: This technique involves slow, deliberate inhalations through the nose, allowing the lungs to fill completely, followed by a controlled exhalation through the mouth or nose. The focus on breath helps divert attention from stressors, activates the parasympathetic nervous system, and lowers heart rate. A common method is diaphragmatic breathing, where the abdomen rises with each inhale and falls with each exhale, encouraging full oxygen exchange and relaxation.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR): PMR involves systematically tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups in sequence. Starting from the feet and working upward, each group is contracted tightly for 5-10 seconds and then released. This process heightens awareness of physical sensations and helps distinguish between tension and relaxation, leading to overall muscular and mental calmness.
- Meditation: Meditation practices focus on cultivating mindfulness or a specific focus point, such as a mantra or breathing pattern. Techniques like guided imagery or body scan meditation can be particularly effective before sleep. Regular meditation reduces cortisol levels, enhances emotional regulation, and prepares the mind for restful sleep by fostering a state of present-moment awareness and tranquility.
Practicing Mindfulness and Stress Management Before Sleep
Mindfulness entails paying deliberate attention to the present moment without judgment, which can significantly diminish pre-sleep anxiety and racing thoughts. Developing a mindful approach involves creating awareness of one’s thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations, thereby preventing stressors from escalating and interfering with sleep.To effectively practice mindfulness before bedtime:
- Set aside a dedicated time, ideally 10-15 minutes, to focus solely on mindfulness exercises.
- Find a quiet, comfortable space free from distractions.
- Adopt a relaxed seated or lying position, closing your eyes if comfortable.
- Begin with deep, slow breaths to anchor your attention in the present moment.
- Progress to body scan techniques, gradually bringing awareness to different parts of the body, noting sensations, tension, or relaxation.
- When intrusive thoughts arise, acknowledge them without judgment and gently redirect focus back to your breath or bodily sensations.
This practice helps reduce physiological arousal and mental clutter, leading to a calmer mind ready for sleep.In addition, effective stress management involves establishing a wind-down routine that minimizes stimulating activities, limits screen time, and encourages calming hobbies such as reading or listening to gentle music. Incorporating these techniques consistently can greatly enhance sleep quality and overall well-being.
Managing Sleep Disruptors and Sleep Disorders

Effective sleep hygiene involves understanding and managing factors that can interfere with restful sleep. Sleep disruptors and underlying sleep disorders are common challenges that, if unaddressed, can significantly impair overall well-being. Recognizing these issues early and implementing appropriate strategies can improve sleep quality without the need for medication. This section explores common sleep disruptors, offers practical mitigation techniques, and provides guidance on identifying and responding to signs of sleep disorders.
Addressing sleep disruptors involves both lifestyle adjustments and awareness of potential health concerns. While occasional disturbances are normal, persistent issues may indicate underlying sleep disorders that require attention. Learning to distinguish normal disruptions from clinical conditions empowers individuals to seek timely support and adopt targeted solutions. A structured approach helps in managing ongoing sleep problems effectively, ensuring better restorative sleep and overall health.
Common Sleep Disruptors and Strategies to Mitigate Their Effects
Understanding the factors that interrupt sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy sleep cycle. Various external and internal factors can act as sleep disruptors, often exacerbated by modern lifestyles. Implementing strategies to reduce or eliminate these disturbance sources can significantly improve sleep quality.
- Caffeine and Stimulants: Consumption of caffeine, nicotine, or other stimulants close to bedtime can delay sleep onset and reduce sleep efficiency. To mitigate effects, limit caffeine intake after early afternoon and avoid nicotine in the evening.
- Electronic Devices and Screen Time: The blue light emitted from screens suppresses melatonin production, delaying sleep. Establish a technology curfew at least one hour before bed, and consider using blue light filters or glasses.
- Noise and Light Pollution: Excess noise and light can fragment sleep and decrease its restorative quality. Use blackout curtains, sleep masks, or white noise machines to create a more conducive sleep environment.
- Irregular Sleep Schedules: Frequent changes in sleep timing can disrupt circadian rhythms. Aim for consistency by going to bed and waking up at the same times daily, even on weekends.
- Heavy Meals and Alcohol: Eating large meals or consuming alcohol before bed can interfere with sleep architecture. Opt for light, easily digestible snacks and limit alcohol intake in the evening.
Identifying and Addressing Signs of Sleep Disorders
While most sleep disturbances are temporary, persistent issues may suggest underlying sleep disorders such as insomnia, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or narcolepsy. Recognizing early signs allows for timely intervention, often through lifestyle modifications or consultation with healthcare professionals, without immediate reliance on medication.
- Monitoring Sleep Patterns: Keep a sleep diary for at least two weeks, noting bedtimes, wake times, nighttime awakenings, and daytime sleepiness. Patterns may reveal specific issues requiring attention.
- Assessing Daytime Functioning: Consider how sleep quality affects mood, concentration, energy levels, and overall functioning. Persistent fatigue, irritability, or impaired cognitive performance are common indicators of sleep disturbances.
- Recognizing Physical Symptoms: Snoring, observed pauses in breathing during sleep, restless movements, and leg discomfort may point to sleep apnea or other conditions needing medical evaluation.
- Seeking Professional Evaluation: When symptoms persist despite behavioral adjustments, consult a sleep specialist. Diagnostic tools like polysomnography can identify specific disorders and inform appropriate, non-pharmacological treatment options.
Flowchart of Steps for Persistent Sleep Issues
When sleep problems continue despite implementing lifestyle and environmental adjustments, following a structured pathway ensures appropriate management and escalation when necessary. Below is an Artikel of recommended steps:
Step 1: Continue tracking sleep patterns and reinforcing sleep hygiene practices.
Step 2: If sleep problems persist for more than three weeks or worsen, consult a primary care provider or sleep specialist.
Step 3: Undergo comprehensive sleep assessment, including medical history review and possible sleep studies.
Step 4: Based on diagnosis, explore behavioral therapies such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I), lifestyle modifications, or non-invasive interventions.
Step 5: Regular follow-up to monitor progress and adjust strategies as needed, avoiding reliance on medications unless prescribed by a healthcare professional for specific conditions.
Tracking and Improving Sleep Quality
Maintaining awareness of sleep patterns through consistent tracking is a vital step toward enhancing sleep quality naturally. By systematically recording sleep data, individuals can identify patterns, recognize disruptions, and implement targeted strategies to foster healthier sleep habits. This proactive approach empowers you to make informed adjustments and set achievable goals for better rest.
Implementing a structured sleep journal or tracker allows for detailed documentation of sleep behaviors and environmental factors that influence sleep quality. Analyzing this data over time reveals trends and potential issues, such as inconsistent bedtimes or frequent awakenings. Based on these insights, realistic and personalized sleep goals can be established, promoting gradual and sustainable improvements in sleep health.
Designing a Sleep Journal or Tracker Template
Creating an effective sleep tracker involves setting up a clear and comprehensive template that captures relevant sleep-related information daily. The following HTML table example provides a simple yet detailed structure to record key data points:
| Date | Time Went to Bed | Time Fell Asleep | Number of Awakenings | Wake-Up Time | Total Sleep Duration | Sleep Quality (1-10) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024-04-20 | 10:30 PM | 10:45 PM | 2 | 6:30 AM | 7 hrs 45 mins | 7 | Felt rested, slight difficulty falling asleep initially |
| 2024-04-21 | 11:00 PM | 11:15 PM | 1 | 7:00 AM | 7 hrs 45 mins | 8 | Stayed asleep most of the night |
This template can be customized to include additional factors such as caffeine intake, exercise, or stress levels that may affect sleep quality. Maintaining consistent entries enhances the accuracy of your data and provides a reliable basis for analysis.
Analyzing Sleep Data to Identify Patterns and Areas for Improvement
Regular review of your sleep journal is essential for uncovering patterns that might hinder restful sleep. By examining your recorded data, you can identify correlations between specific behaviors or environmental factors and sleep quality. For example, noticing frequent awakenings on nights when caffeine is consumed after 3 PM or when stress levels are high can guide behavioral adjustments.
Look for trends such as inconsistent bedtimes, irregular sleep durations, or frequent disruptions. Employing simple analysis methods like calculating average sleep duration over a week or noting the times with the highest sleep quality scores helps pinpoint areas needing attention. Recognizing these patterns allows for targeted interventions designed to optimize your sleep environment and routines.
“Data-driven insights are the foundation of effective sleep improvement strategies. Consistent tracking transforms subjective perceptions of sleep into objective, actionable information.”
Setting Realistic Sleep Goals Based on Tracked Data
Using your analyzed sleep data, set achievable and personalized goals that foster gradual improvement. For example, if your average sleep duration is around 6.5 hours, a realistic target may be increasing it to 7 hours over a few weeks. Establishing specific goals, such as going to bed 15 minutes earlier each night, helps create manageable milestones.
It is important to consider individual needs and lifestyle constraints when setting these goals. Consistency is key; aim for steady progress rather than abrupt changes, which can be counterproductive. Regularly reviewing your tracked data will enable you to adjust your sleep goals as you observe improvements or encounter new challenges, ensuring your approach remains flexible and effective.
Final Thoughts
Embracing natural sleep improvement techniques provides a sustainable and health-friendly alternative to medication. By understanding your sleep cycles, creating a peaceful environment, and adopting calming habits, you can enjoy more restful nights. Consistency and mindfulness are key to transforming your sleep patterns and experiencing rejuvenation every morning.